File Read Write
The purpose of the File Read Write rule is to allow you to restrict a protected application from reading or writing to any file to which it should not have access.
Overview
This rule could prevent an application from reading a password file or writing to the shadow file on the system on which it resides. This protection isn't specific to a CWE or other defined or limited attack. The method of attack that causes the protected application to attempt to execute a specific command is irrelevant to this rule. This rule only looks at and potentially protects against the end result of any such attack.
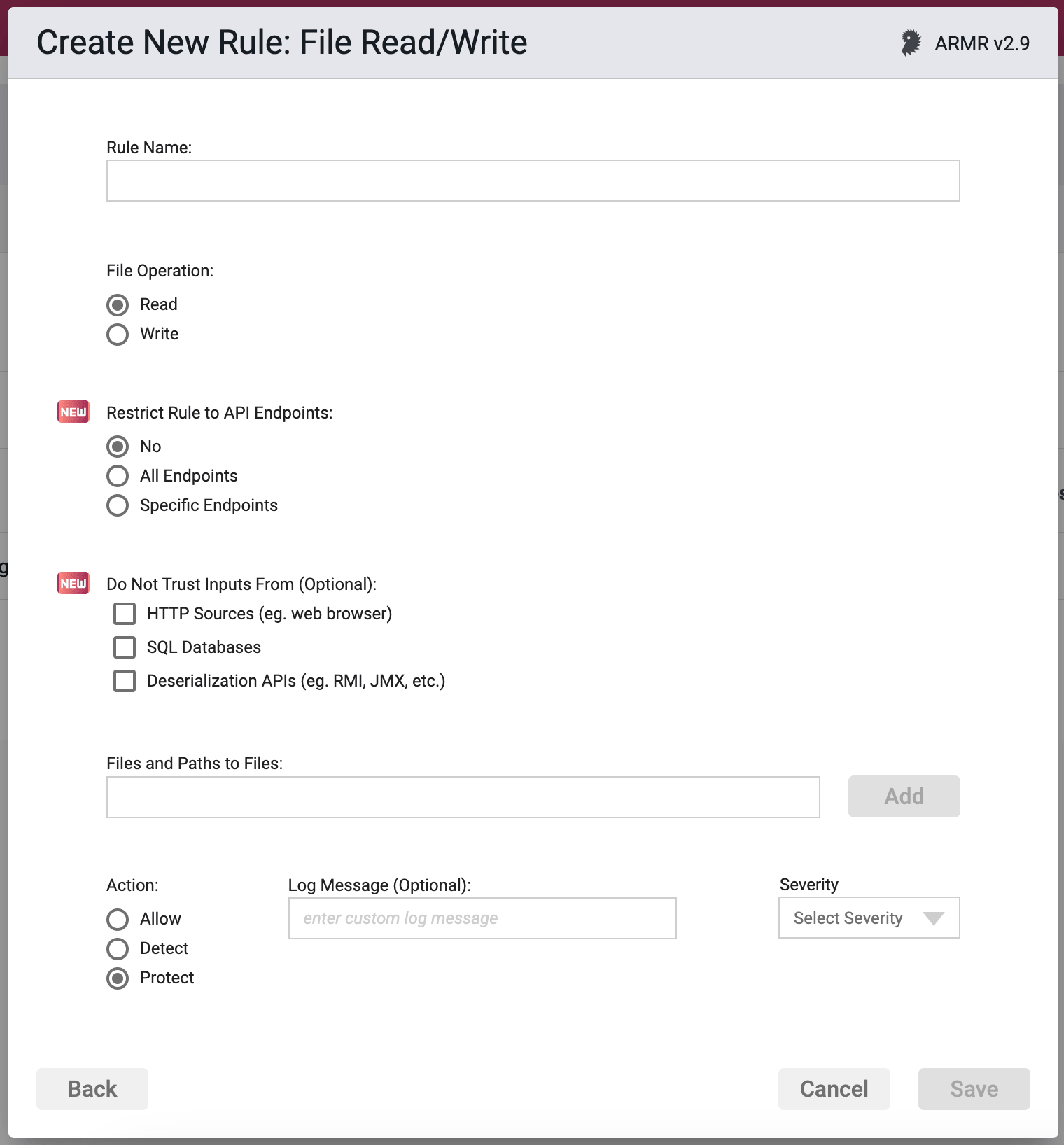
Rule Options
File Operation
The only options here are read or write. This tells the rule which action it is controlling, the reading of files or paths, or the writing to files or paths.
Restrict Rule to API Endpoints
You can limit the rule to respond to API requests only.
- No - Do not restrict the rule response
- All Endpoints - Restrict the rule response to API requests only
- Specific Endpoints - Restrict the rule response to API requests on the specified endpoints
You can change the default value No but you can select only one of these options.
Do Not Trust Inputs From
Protection can be, optionally, limited to lookup that contain untrusted input. If no inputs are selected, protection is applicable to all files, no matter how this file was obtained by the Application.
Sources that the strict policy option will treat as untrusted are:
HTTP - Data received by the application from HTTP requests (e.g. from a web browser).
SQL Databases - Data received by the application from a SQL database.
Java Deserialization APIs - Data received by the application via deserialization APIs (e.g. RMI, JMX, Java Object Deserialization, etc.)
It is not possible to create an Allow rule which would only be applicable in the context of processing API requests. Restricting the rule to specific endpoints will remove the Allow action option.
Selecting input(s) not to trust will also remove the Allow action option. The Allow action can only be specified for the file operation, and it can not be limited to any single trusted input source.
See the API Protect section of the ARMR documentation for further details.
Files and Paths to Files
Here you can type in a path(s) or specific files that the rule will apply to. Generally speaking this can be applied in 2 different ways:
- You can list a number of paths and/or files that you wish to prevent from being read or written to via the protect action, or
- You can create a pair of rules where the first File Read Write rule uses a path to Protect (e.g.
/etc/*), and the second Process Rule allows or whitelists specific files (via the Allow/Whitelist action) contained within that path, such as/etc/someTextFile.txt.
This way if there are 100 files in the target directory and you wish to protect 98 of them, you do not have to create 98 rules or an unwieldy rule listing 98 files. You can instead create 1 rule to protect against all of the files within the target directory, and create another rule to carve out the 2 that you want to allow to be read or written to.
In essence, the Allow/Whitelist option is allowing us to say “Protect all of these files” (protect rule with a path entered) followed by “Except these” (allow rule, explicitly listing files within that path). This is much more scalable than saying “Protect this file” (standard rule) 98 times.
You can type paths or files into the text field and upon typing a comma, or hitting the Return/Enter key the entries will be accepted and converted to a pill object which can then be removed from the list by clicking on the pill's cross symbol (x).
Action
- Detect - The Agent will detect the reading or writing of listed file (or files within a path), log the event to the event database, and the event will be viewable on the Security Events pages in the Portal, but the Agent will take no further action.
- Protect - In addition to the Detect actions, the Waratek Agent will also actively prevent the reading or writing of the files or anything within the protected paths, from succeeding.
- Allow - Acts as whitelist. This is similar to the Detect action in that no blocking or destructive action will be taken, however the Allow action will supersede the Protect action by whitelisting files and paths to be excluded from Protect actions.
If a rule is superseded by a similar rule that has a higher precedence (e.g. targets the same path on the filesystem but with a different action specified) then the rule with lower precedence is skipped by the Agent.
Log Messaging
The logs provide a message field, which can be customized. Text entered here is the message that will be seen on the log files when the rule has been triggered, regardless of the Action. If the field is left blank, then the default logging message will be displayed in the message portion of the event log.
Severity
The log files allow you to select a custom severity level for the event: Low, Medium, High or Critical. A severity is required, and there is no default selection.
Advanced Options
Disable Logging - By checking this option, no logging will be performed when a rule is triggered. Subsequently the Portal will not see these events, and they will not appear anywhere in the Portal, nor will they be searchable in Event Storage.
This option will be greyed out if the rule action is set to Detect.
Enable Stack Trace - By checking this option, when a rule is triggered, the stack trace will be included in the event log, and will be available for viewing in the Portal UI for each triggering security event.